Business Sustainability in the Circular Economy (RH/UoL)
Contents
https://www.coursera.org/learn/business-sustainability-circular-economy
- Lower food miles is not necessarily better - green beans grown in Kenya (hand-raised, natural fertilisers) and flown to the UK may emit less than those grown in the UK (tractors, oil-based fertilisers).
- Emissions from the entire supply chain must be considered, and the bottom of the pyramid (the most distant suppliers in the supply chain) are usually hardest.
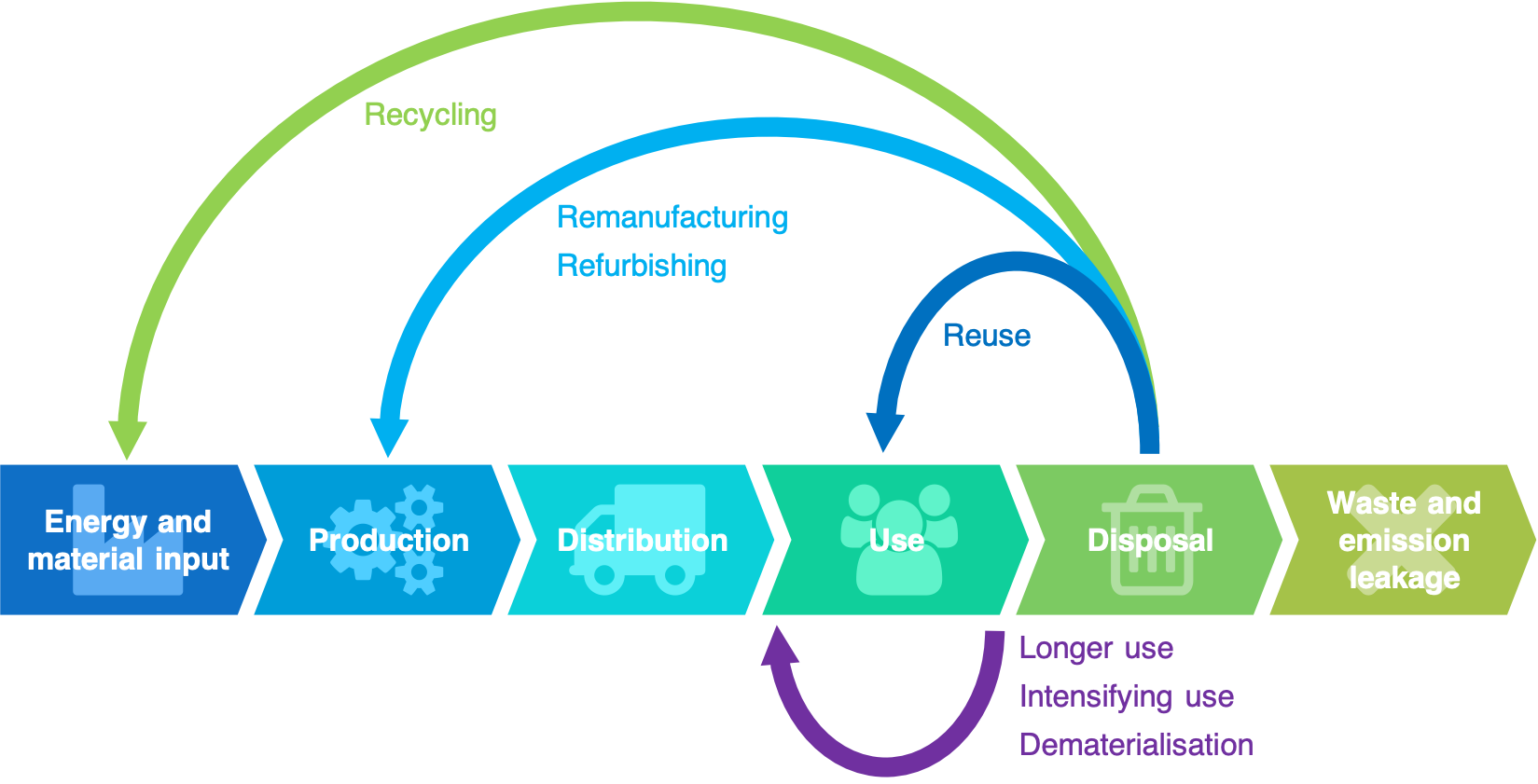
- Linear (take, make, dispose) vs circular (make, use, return) → reduces virgin material use (and hence mining etc), reduces landfill (and hence emissions and waste)
- Reverse logistics (getting something back to the supplier)
- What: End-of-use product or packaging
- Why: For recycling, repurposing, reuse
- How: More complicated than forward logistics due to uncertainty (when, where, what (condition), etc) so often use third-party logistcs (3PL) companies
- Who: B2B is easier than B2C
- New legislation
- Design must consider end-of-life dismantling for recycling/reuse
- Right to repair